Best Application Modernization Solutions: Top 5 in 2025
What Are Application Modernization Solutions?
Application modernization solutions involve updating and improving existing software and processes to leverage modern technologies and strategies. This can include migrating to the cloud, adopting microservices architectures, and improving security and scalability. The goal is to improve business agility, reduce costs, and enhance performance.
Modernizing applications typically involves moving from monolithic architectures to more modular ones, integrating cloud-native technologies, and automating infrastructure management. The aim is to improve performance, reduce operational costs, and support innovation while maintaining business continuity.
Organizations pursue application modernization to overcome limitations imposed by outdated systems such as inflexibility, security risks, and the high cost of maintenance. By deploying modernization solutions, organizations enable faster development cycles, easier integration with new technologies, and better user experiences.
Key Features of Application Modernization Solutions
Architecture Transformation
Architecture transformation involves converting rigid, monolithic systems into flexible, loosely coupled architectures. This often requires adopting microservices, containerization, and serverless computing, which enable faster deployment, improved scalability, and easier updates. The process starts with assessing the current architecture, identifying bottlenecks or dependencies, and then redesigning the application to break down silos and reduce complexity.
With new architectural patterns, organizations achieve greater agility and resilience. Microservices make it easier to scale individual components, while containers ensure consistency across development, testing, and production environments. Architecture transformation also lays the groundwork for future improvements.
Application Understanding
Application understanding is the process of analyzing and documenting how an existing system works before making modernization changes. It involves examining application dependencies, data flows, integrations, and business logic to identify what can be optimized, replaced, or retired. Without this step, modernization efforts risk breaking critical functionality or overlooking hidden dependencies.
Techniques such as code analysis, dependency mapping, and business rule extraction are often used to gain insights into how applications behave in production. These tools help uncover performance bottlenecks, redundant components, and critical functionality.
A clear understanding of the application landscape allows teams to prioritize modernization efforts, estimate costs, and define the right approach—whether rehosting, refactoring, replatforming, or replacing. This structured knowledge reduces uncertainty and ensures modernization aligns with business goals.
Cloud and Infrastructure Modernization
Legacy infrastructure typically constrains scalability and agility due to hardware dependencies and maintenance burdens. By migrating applications to cloud platforms—public, private, or hybrid—organizations can leverage on-demand resources, automated scaling, and high availability.
As part of modernization initiatives, organizations often adopt cloud-native services like managed databases, storage, and orchestration platforms. Infrastructure as code (IaC) further simplifies provisioning and management, allowing rapid deployment and consistent environments.
Automation and DevOps Enablement
Automation and DevOps enablement are key drivers of accelerated software delivery and improved operational consistency. Modernization solutions typically integrate CI/CD pipelines, automated testing, and infrastructure orchestration to reduce manual intervention and minimize errors. This approach ensures that new features, updates, and fixes are deployed rapidly, safely, and frequently.
DevOps philosophies foster collaboration between development and operations teams, breaking down traditional silos. By using automation tools and standardized workflows, teams simplify processes, monitor applications proactively, and respond to incidents with speed and precision. This results in higher software quality, faster recovery from failures, and a culture of continuous improvement.
API and Integration Layers
API management and integration layers connect modernized applications with other systems, services, and data sources. Application modernization often includes exposing core functionalities as APIs, enabling seamless integration with both internal and external platforms. An effective API layer simplifies communication, supports microservices, and accelerates the delivery of new digital services.
Robust integration frameworks handle diverse protocols, data formats, and authentication methods, making hybrid deployments and third-party connectivity more manageable. With secure API gateways and monitoring tools, organizations maintain control over usage and performance.
Security and Compliance
Legacy systems often have outdated protections and growing exposure to threats. Modernization solutions include advanced security features such as automated vulnerability scanning, identity management, encryption, and policy enforcement. These capabilities protect sensitive data and applications from unauthorized access, breaches, and emerging cyber risks. Compliance is increasingly important, particularly for organizations in regulated industries.
Modernized environments incorporate tools for auditing, monitoring, and maintaining regulatory requirements such as GDPR or HIPAA. These features help organizations mitigate risk, avoid penalties, and maintain trust with customers and partners. By integrating security and compliance from the start, organizations ensure business resilience and regulatory readiness throughout the modernization journey.
Related content: Read our guide to application modernization tools (coming soon)
Notable Application Modernization Solutions
1. Swimm

Swimm’s Application Understanding Platform addresses one of the biggest challenges in modernization — the lack of clear visibility into existing applications. By combining deterministic static analysis with generative AI, Swimm translates legacy code into reliable, human-readable knowledge that teams can act on with confidence. The platform is designed for highly secure enterprise environments, making it suitable for banks, insurers, and other regulated industries.
Key features include:
- Business rule extraction: Reliably uncovers and explains the business logic hidden within legacy codebases.
- Architectural overviews: Maps application architectures, breaking down programs, jobs, flows, and dependencies into clear visual structures.
- Natural language translation: Converts cryptic program and variable names into descriptive, easy-to-understand terms for faster comprehension.
- Customizable support: Handles complex and proprietary implementations of COBOL, CICS, and PL/I with specialized parsers and company-specific plug-ins.
- Trust and reliability: Deterministic static analysis prevents LLM hallucinations, ensuring accurate insights across millions of lines of code.
Swimm equips business, architecture, and engineering teams with the clarity they need to modernize systems quickly, securely, and cost-effectively.
2. Google Cloud Application Modernization

Google Cloud’s application modernization solutions provide a structured, data-driven approach to upgrading legacy systems while minimizing risk and maximizing return on investment. The offering combines automated assessment, planning, and migration tools with proven DevOps practices, enabling organizations to modernize at their own pace.
Key features include:
- CAMP Framework: Guides modernization using Google’s experience and DORA’s research to assess, plan, and improve software practices.
- Hybrid and multicloud platform: Provides consistent development and operations across environments with policy management capabilities.
- Cloud-native development: Enhances developer productivity with an end-to-end platform, built-in security, and reduced operational overhead.
- Serverless computing: Fully managed environment that auto-scales with traffic, simplifying deployment and orchestration.
- DevOps enablement: Improves deployment speed, reliability, and security with integrated CI/CD and collaboration tools.
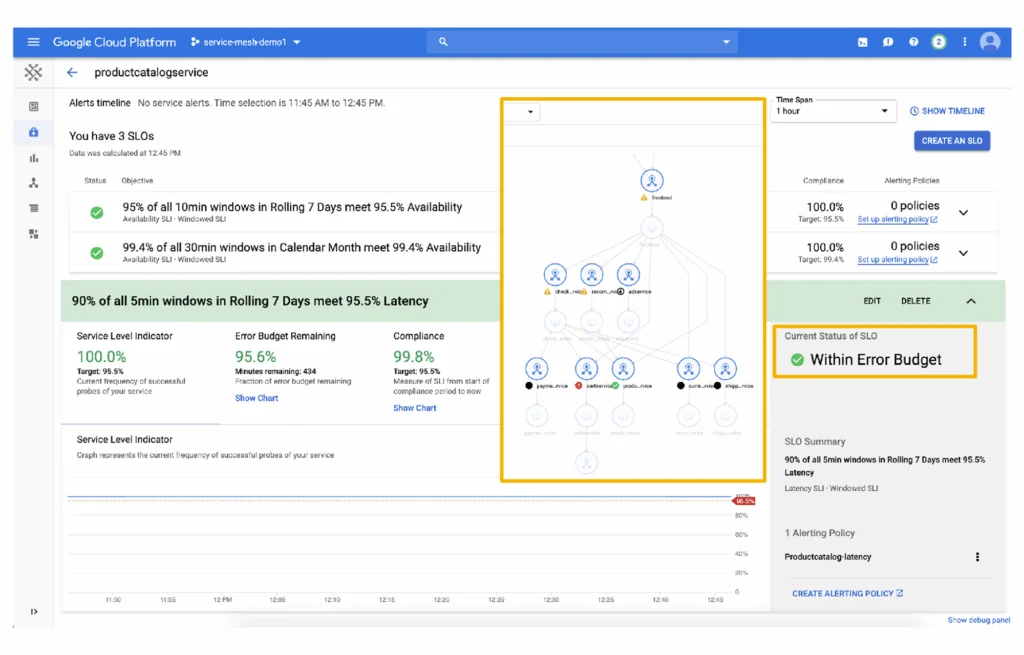
Source: Google Cloud
3. Rocket Software

Rocket Software offers a portfolio of modernization solutions across hybrid cloud, security and compliance, skills and efficiency, and data. Offerings are positioned to meet organizations at any point in their modernization journey, with global reach and partnerships.
Key features include:
- Modernization portfolio: Includes hybrid cloud, security and compliance, optimizing skills and efficiency, and data solutions addressing multiple modernization needs.
- Engagement approach: Meets organizations wherever they are in the modernization journey, rather than prescribing a single starting point or path.
- Experience and expertise: Brings over 30 years of modernization experience to guide complex transformations with established practices and domain knowledge.
- Global delivery: Combines global reach with local expertise, supported by a partner network intended to match local environments and requirements.
- Continuous innovation: Emphasizes ongoing investment in technologies to keep systems current as modernization progresses and enterprise priorities evolve.
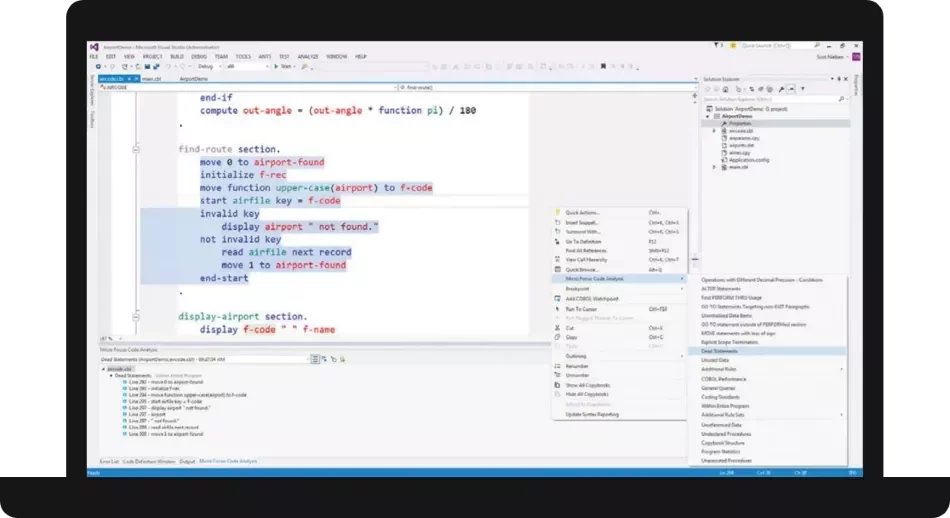
Source: Rocket Software
4. IBM Application Modernization
IBM provides application modernization services that apply hybrid cloud and generative AI to modernize and containerize legacy applications. Services use IBM Garage methodology and the IBM Consulting Advantage for Cloud Transformation platform, supported by partnerships across major cloud providers.
Key features include:
- Modernization roadmap: Co-creates roadmaps using IBM Garage methodology and patterns such as rehosting, refactoring, replatforming, rearchitecting, or replacing applications.
- Generative AI acceleration: Uses IBM Consulting Advantage for Cloud Transformation to generate code, support containerization and microservices, and scale modernization with consistency and speed.
- Cloud migration services: Designs secure, repeatable, and scalable migration strategies to boost performance, scalability, and cybersecurity for cloud adoption.
- Mainframe modernization: Modernizes existing mainframe applications and data, extends them to cloud, and integrates with existing systems while supporting new cloud-native development.
- Strategic partnerships: Works with AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud using methodologies, reusable blueprints, and tools for design, migration, and operations.
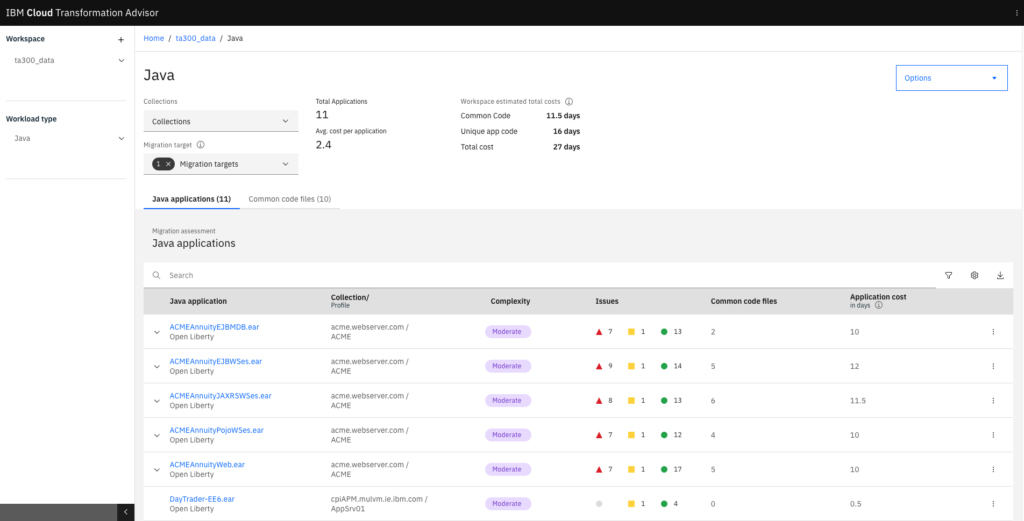
Source: IBM
5. CAST

CAST analyzes codebases to map internal architecture and dependencies into a living knowledge base. Semantic analysis reverse-engineers interactions across databases, components, transactions, and frameworks to support discovery, impact assessment, and modernization planning.
Key features include:
- Semantic analysis and mapping: Builds a living knowledge base of application elements and interactions, reverse-engineering dependencies across layers and technologies.
- Architecture exploration: Displays real-time internal architecture, identifies functional communities, obsolete technologies, and decoupling candidates, including potential microservices boundaries and tightly or loosely coupled modules.
- Impact monitoring: Assesses effects of new or changed code, tracks adherence to intended designs, and evaluates structural quality implications for planned isolation or separation.
- Pathway tracing: Produces data access graphs and API call graphs, highlighting hard-to-separate dependencies and low-dependency flows to guide refactoring, rearchitecting, and migration decisions.
- Collaboration features: Allows tagging components and modules with functional knowledge, such as transactions and decoupling targets, to share modernization context across teams.
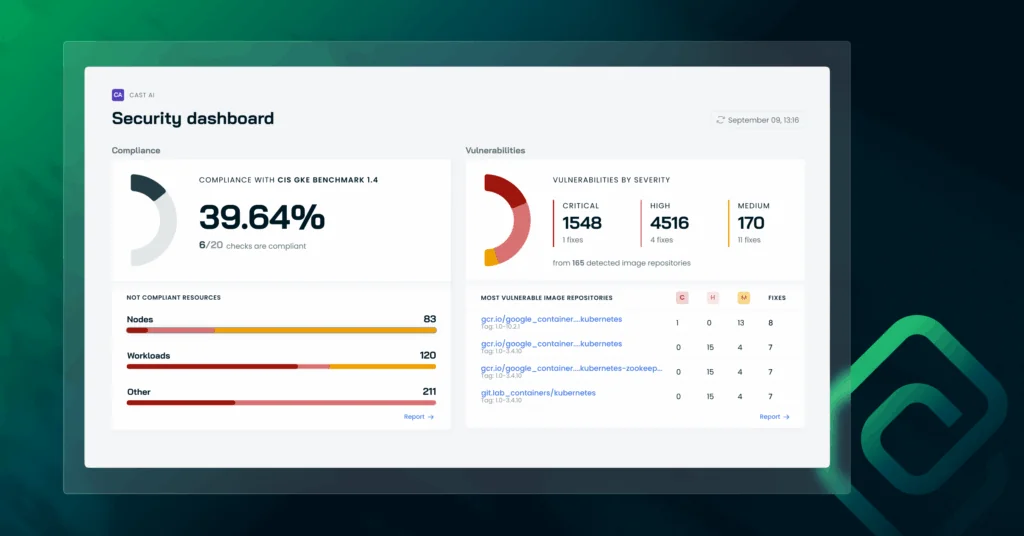
Source: CAST
Considerations for Choosing Application Modernization Solutions
Choosing the right application modernization solution requires aligning technical capabilities with business priorities while managing cost, risk, and long-term maintainability. The decision should consider the current application landscape, organizational readiness, and the speed at which change can be adopted without disrupting operations. A balanced approach weighs immediate gains against the potential for future scalability and adaptability.
Key considerations include:
- Compatibility with existing systems: Ensure the solution integrates with current infrastructure, data sources, and workflows without forcing disruptive changes.
- Migration approach: Decide between rehosting, re-platforming, refactoring, or full replacement based on application complexity, technical debt, and business urgency.
- Cloud strategy alignment: Verify that the solution supports your preferred deployment model (public, private, hybrid, or multicloud) and leverages relevant cloud-native capabilities.
- Security and compliance requirements: Confirm that security controls, encryption standards, and compliance tooling meet industry regulations and internal governance needs.
- Automation and DevOps support: Look for features that enable CI/CD pipelines, automated testing, and infrastructure orchestration to maintain speed and consistency.
- Vendor expertise and support: Assess the provider’s track record, industry knowledge, and ongoing support model for modernization projects.
- Total cost of ownership (TCO): Consider not only initial licensing and migration costs but also long-term maintenance, scaling expenses, and operational efficiencies.
- Scalability and future-proofing: Select solutions that can adapt to new business models, emerging technologies, and increased demand without costly redesigns.
- Change management and skills enablement: Evaluate whether the solution includes training, documentation, and process support to help teams adopt new technologies effectively.
Conclusion
Application modernization solutions provide a structured path for transforming outdated systems into agile, secure, and scalable platforms. By addressing architectural bottlenecks, integrating cloud-native technologies, and embedding automation, these solutions help organizations reduce technical debt while enabling faster delivery of digital services. The result is an IT environment that can adapt to evolving business needs, support innovation, and maintain resilience in a rapidly changing technology landscape.