What Is Application Modernization Software?
Application modernization software refers to tools and platforms that help organizations update legacy software systems and bring them in line with modern computing standards. These solutions transform older applications, which are often built on outdated, monolithic architectures, into cloud-native, modular, and scalable systems.
They enable organizations to leverage new technologies, integrate with contemporary infrastructure, and support digital transformation initiatives while mitigating the cost and risk of full system replacements. Modernization software typically provides features such as automated code analysis, re-platforming, containerization, and process orchestration.
These capabilities help teams refactor, re-host, or re-architect legacy systems more efficiently. Through automation, best practice frameworks, and guided workflows, these tools reduce manual effort and human error, simplifying the journey from legacy environments to flexible, modern architectures.
Why Organizations Modernize Applications
Modernizing applications is not only about replacing outdated technology—it is about ensuring that systems remain competitive, secure, and capable of supporting evolving business needs. Legacy systems often become a bottleneck, limiting innovation and increasing operational risks. Modernization enables organizations to adapt faster, reduce costs, and deliver better experiences to users and customers.
Key reasons for application modernization
- Reduce maintenance costs: Older applications often require specialized skills, expensive licenses, and frequent patching. Modernizing reduces ongoing maintenance expenses by moving to standardized, widely supported platforms.
- Improve performance and scalability: Legacy architectures struggle with large-scale workloads and sudden demand spikes. Modernized applications can scale horizontally in cloud environments, delivering faster response times and higher availability.
- Enhance security and compliance: Outdated software can contain unpatched vulnerabilities and may not meet current regulatory requirements. Modernization allows integration of modern security frameworks and adherence to compliance standards.
- Enable integration with modern systems: Legacy systems may use proprietary protocols or outdated data formats, making integration difficult. Modernized applications use APIs and microservices to connect with contemporary tools and platforms.
- Support digital transformation initiatives: Many transformation projects—such as AI adoption or omnichannel customer engagement—require flexible, modern infrastructure. Modernization provides the foundation for these initiatives.
- Extend application lifespan: Rather than replacing systems entirely, modernization refreshes core components, extending the usefulness of critical applications while maintaining business continuity.
- Improve developer productivity: Legacy codebases can slow development cycles due to complexity and outdated practices. Modernization introduces modern frameworks, automation, and CI/CD pipelines, enabling faster delivery of new features.
Key Features and Capabilities of Application Modernization Software
Microservices and API Enablement
Microservices and API enablement are central to most modernization efforts, breaking down monolithic applications into discrete, independently deployable components. Modernization tools help identify logical boundaries within legacy systems, enabling decomposition into microservices that communicate over standardized APIs. This approach supports modular development, easier maintenance, and the ability to update or scale services in isolation.
By enabling APIs, legacy applications can interact seamlessly with modern environments, external services, and partner ecosystems. Tools often automate the exposure of business functionality via secure REST or GraphQL endpoints, promoting reuse and system interoperability.
AI-Assisted Modernization
AI-assisted modernization leverages artificial intelligence to automate the assessment, transformation, and optimization of legacy codebases. These tools can analyze millions of lines of code to identify dependencies, recommend refactoring strategies, and even generate migration plans. AI can also highlight redundant or dead code, improving the quality and maintainability of the modernized application.
Beyond code transformation, AI-powered platforms can simulate modernization outcomes and forecast performance or cost implications. Automation-driven insights accelerate project timelines and reduce error rates, ensuring that modernization efforts yield efficient, future-proof applications.
Cloud and Infrastructure Migration
Cloud and infrastructure migration are essential capabilities, enabling organizations to transition legacy workloads to public, private, or hybrid cloud environments. Modernization software helps re-platform applications, shifting them from physical or virtual machines to containers or serverless platforms. These tools automate aspects of provisioning, configuration, and deployment, simplifying the migration process and minimizing downtime.
In addition to moving workloads, good modernization software ensures application compatibility with new infrastructure, optimizing for scalability and resilience in the target environment. Automated testing and resource allocation features further mitigate migration risks.
DevOps and CI/CD Support
DevOps and CI/CD support are crucial for continuous improvement and rapid delivery of modernized applications. Modernization platforms integrate with source control, build, and deployment tools to automate pipelines for testing, packaging, and releasing new versions. This integration reduces manual steps, shortens feedback loops, and accelerates time-to-market for new features or fixes.
By enforcing consistent deployment practices and supporting automated rollback mechanisms, these tools improve application reliability. Legacy applications modernized through DevOps pipelines can more easily adopt agile methodologies, enabling iterative updates and faster adaptation to business needs.
Static Analysis and Impact Tracking
Static analysis and impact tracking are essential for safe and efficient modernization projects. Static analysis tools evaluate source code to uncover architectural flaws, vulnerabilities, and potential refactoring opportunities without executing the code. This analysis provides an objective basis for planning modernization activities and identifying technical debt areas that require immediate attention.
Impact tracking complements this by modeling how changes in one component affect the rest of the application and related systems. Modernization solutions help teams visualize interdependencies, assess risk, and prioritize tasks based on their potential business and technical impact.
Business Rule Extraction and Understanding
Business rule extraction and understanding allow organizations to recover critical logic embedded in legacy applications. Over time, business processes often become tightly coupled with code, making them difficult to document or replicate. Modernization tools use parsing and pattern recognition to extract these rules, presenting them in a structured format that is easier to analyze and maintain.
By externalizing business rules, teams can separate decision logic from application code, enabling reimplementation in modern frameworks or rule engines. This ensures that essential business knowledge is preserved during modernization, while also making processes more transparent, adaptable, and easier to update in the future.
Related content: Read our guide to application modernization tools (coming soon)
Application Modernization Software
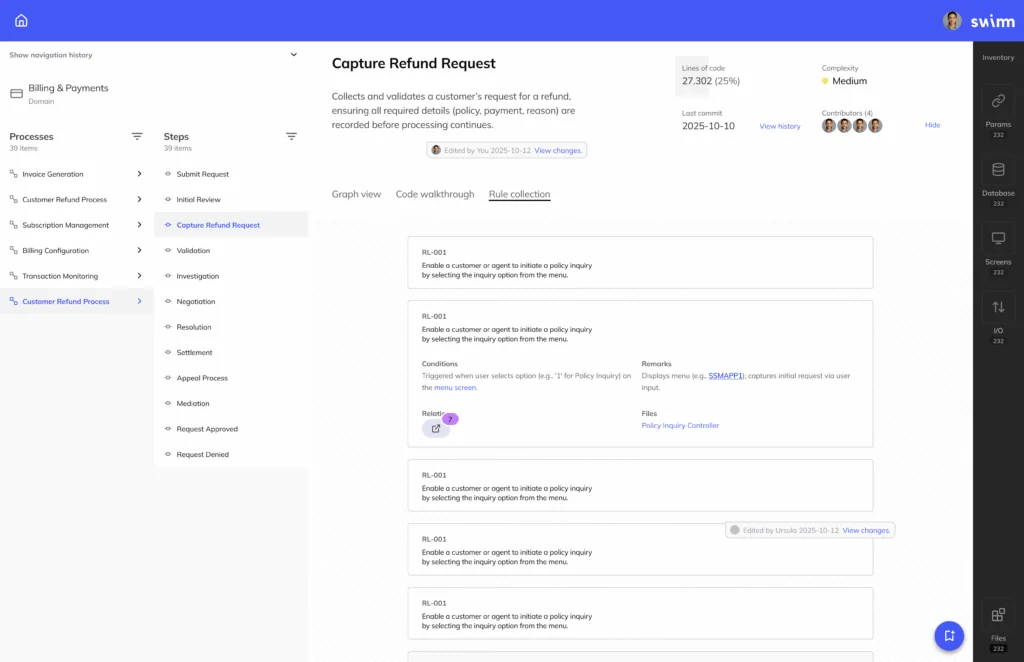
1. Swimm

The Swimm Application Understanding Platform addresses one of the biggest challenges in modernization — the lack of clear visibility into existing applications. By combining deterministic analysis with generative AI, Swimm translates legacy code into reliable, human-readable knowledge that teams can act on with confidence. The platform is designed for highly secure enterprise environments, making it suitable for banks, insurers, and other regulated industries.
Key features include:
- Business rule extraction: Reliably uncovers and explains the business rules spread throughout applications
- Architectural overviews: Maps application architectures, breaking down programs, jobs, flows, and dependencies into clear visual structures.
- Natural language translation: Converts cryptic program and variable names into descriptive, easy-to-understand terms for faster comprehension.
- Customizable support: Handles complex and proprietary implementations of COBOL, CICS, and PL/I with specialized parsers and company-specific plug-ins.
- Trust and reliability: Deterministic static analysis prevents LLM hallucinations, ensuring accurate insights across millions of lines of code.
Swimm equips business, architecture, and engineering teams with the clarity they need to modernize systems quickly, securely, and cost-effectively.
2. Rocket Software

Rocket Software provides a suite of application modernization solutions to help organizations improve customer engagement, improve operational agility, and accelerate innovation. Its tools enable the transition from legacy environments to modern, customer-centric experiences using low-code and no-code development approaches, DevOps automation, and agile CI/CD practices.
Key features include:
- Low-code and no-code development: Build and deploy applications rapidly while reducing manual coding effort.
- DevOps and CI/CD integration: Automate testing, deployment, and operations to improve speed and reliability.
- Customer engagement optimization: Deliver modern, seamless experiences across digital channels to retain and attract users.
- MultiValue platforms: Includes UniData®, UniVerse, jBASE®, and MultiValue Integration Server for database and application development.
- API enablement: Unlock and extend legacy application functionality through Rocket® API for process automation and integration.
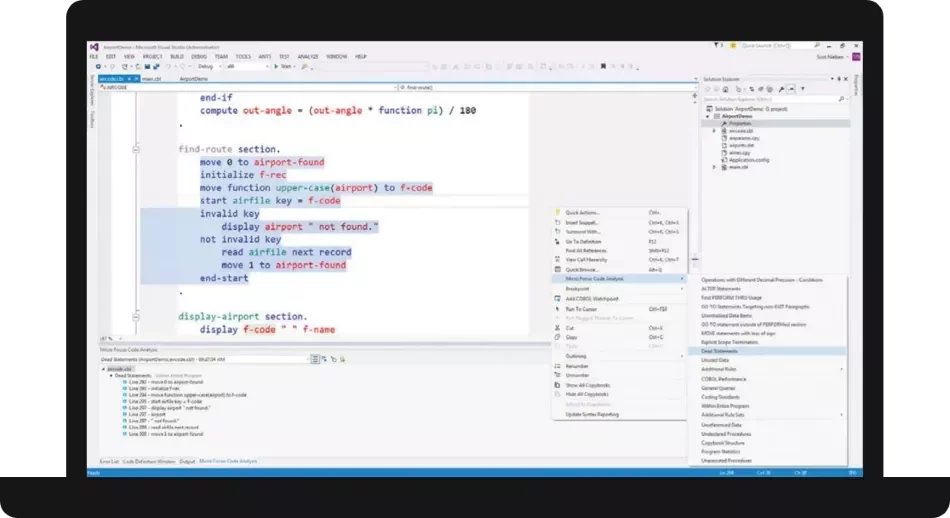
Source: Rocket Software
3. IBM Cloud Pak
IBM Cloud Pak for Applications is an AI-assisted, hybrid-cloud modernization platform that transforms legacy systems into cloud-native applications. Built on Red Hat OpenShift, it enables organizations to modernize runtimes, migrate workloads, and adopt microservices architectures without locking into a single cloud provider.
Key features include:
- Hybrid cloud adoption: Move workloads across on-premises, public, and private cloud environments.
- Runtime modernization: Update and optimize application runtimes to improve efficiency and scalability.
- Workload migration: Migrate legacy workloads with reduced risk of refactoring or rearchitecting.
- Cloud-native development: Leverage microservices and containerization to accelerate build and deployment cycles.
- AI-assisted modernization tools: Automate analysis, migration planning, and optimization to cut migration effort.
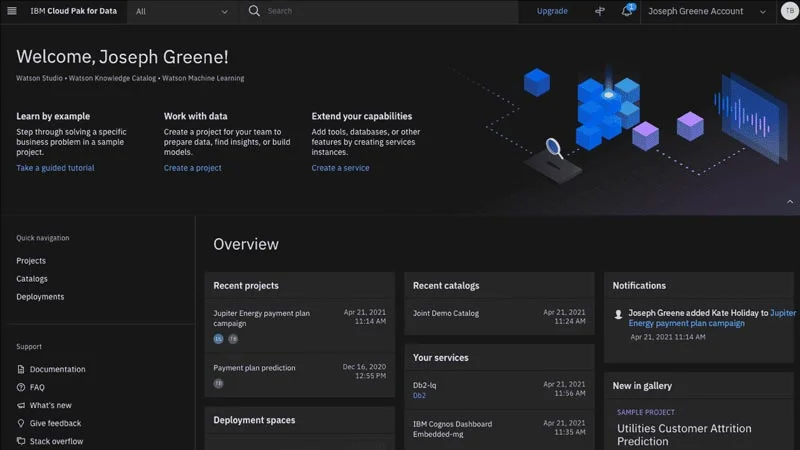
Source: IBM
4. Cast

Cast provides software intelligence for application portfolios and codebases. It includes CAST Highlight for portfolio governance and CAST Imaging for architecture visualization and modernization planning.
Key features include:
- Portfolio governance and technical debt insights: Assess technical debt, cloud readiness, code inefficiencies, and legal exposures across portfolios to prioritize modernization investments and risk mitigation.
- Architecture visualization with CAST Imaging: Map all stack elements and interactions, revealing faulty constructions, dependencies, and change impact to plan safe refactoring and modernization paths.
- Large empirical dataset: Leverages a 25-year dataset including 100 billion lines analyzed and 50,000 relationship heuristics, improving detection across 150+ languages, frameworks, and databases.
- Modernization impact analysis: Simulates modernization paths and identifies ripple effects of changes across components, supporting decisions for replatforming, refactoring, or remediation during complex transformations.
- Stakeholder-specific views: Provides executives, architects, and engineers with portfolio and code-level intelligence, aligning governance and implementation during modernization initiatives.
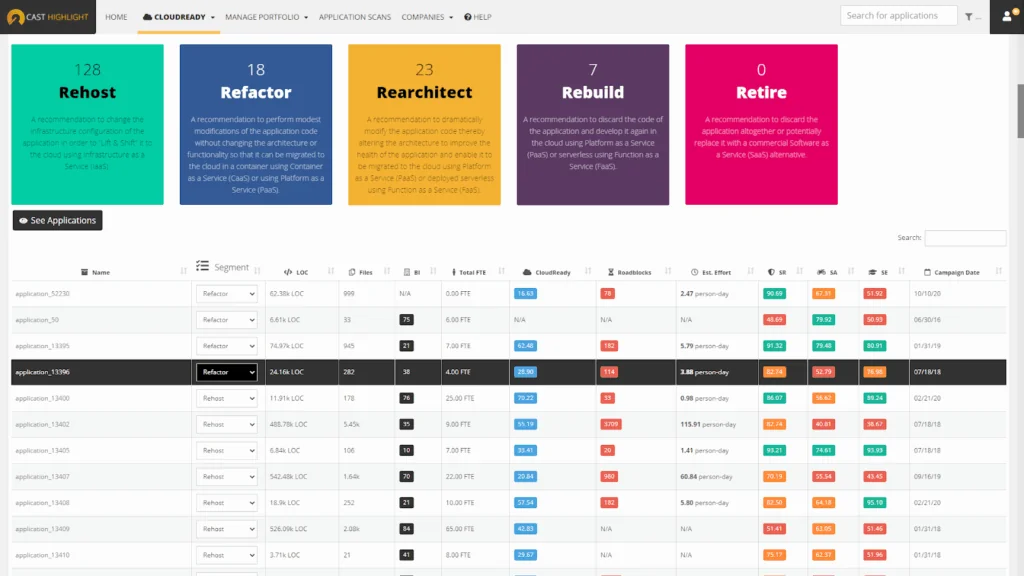
Source: Cast
5. OpenFrame

OpenFrame from TmaxSoft is a mainframe replatforming solution that migrates legacy applications and data to open systems such as Linux, Unix, Docker containers, or public cloud without altering existing business logic. It enables organizations to preserve their application functionality and data while replacing high-cost mainframe environments.
Key features include:
- Future-oriented 3-tier architecture: Provides high performance, stability, and scalability beyond 100K MIPS, supporting next-generation system development.
- Automated conversion with OF Manager: Converts UI logic, application logic, and data without modifying the mainframe source code.
- Language support: Supports COBOL, PL/I, and an Assembler compiler for broad mainframe application coverage.
- Modernization software package: Includes tools for batch, data management, middleware, and operations, along with alternatives for utilities like Sort, Report, and Scheduler.
- Flexible integration: Enables adoption of open-source tools and technologies such as Java, .NET, C++, and Shell scripts.
Conclusion
Application modernization software plays a critical role in enabling organizations to transition from outdated systems to agile, scalable, and cloud-ready environments. These tools simplify complex transformation processes such as rearchitecting, replatforming, and refactoring while minimizing disruption to business operations. With capabilities like automation, AI-driven analysis, and integrated DevOps workflows, modernization software reduces technical debt and prepares applications for continuous innovation and long-term resilience.